Stereochemistry
Overview
1. Chirality.2. Chan-Ingold-Prelog
3. Optical Activity.
4. Enantiomeric Excess
5. Enantiomers and Diastereomers.
1. Chirality
Chiral = have 1 Enantiomer (a non-superimposible mirror image)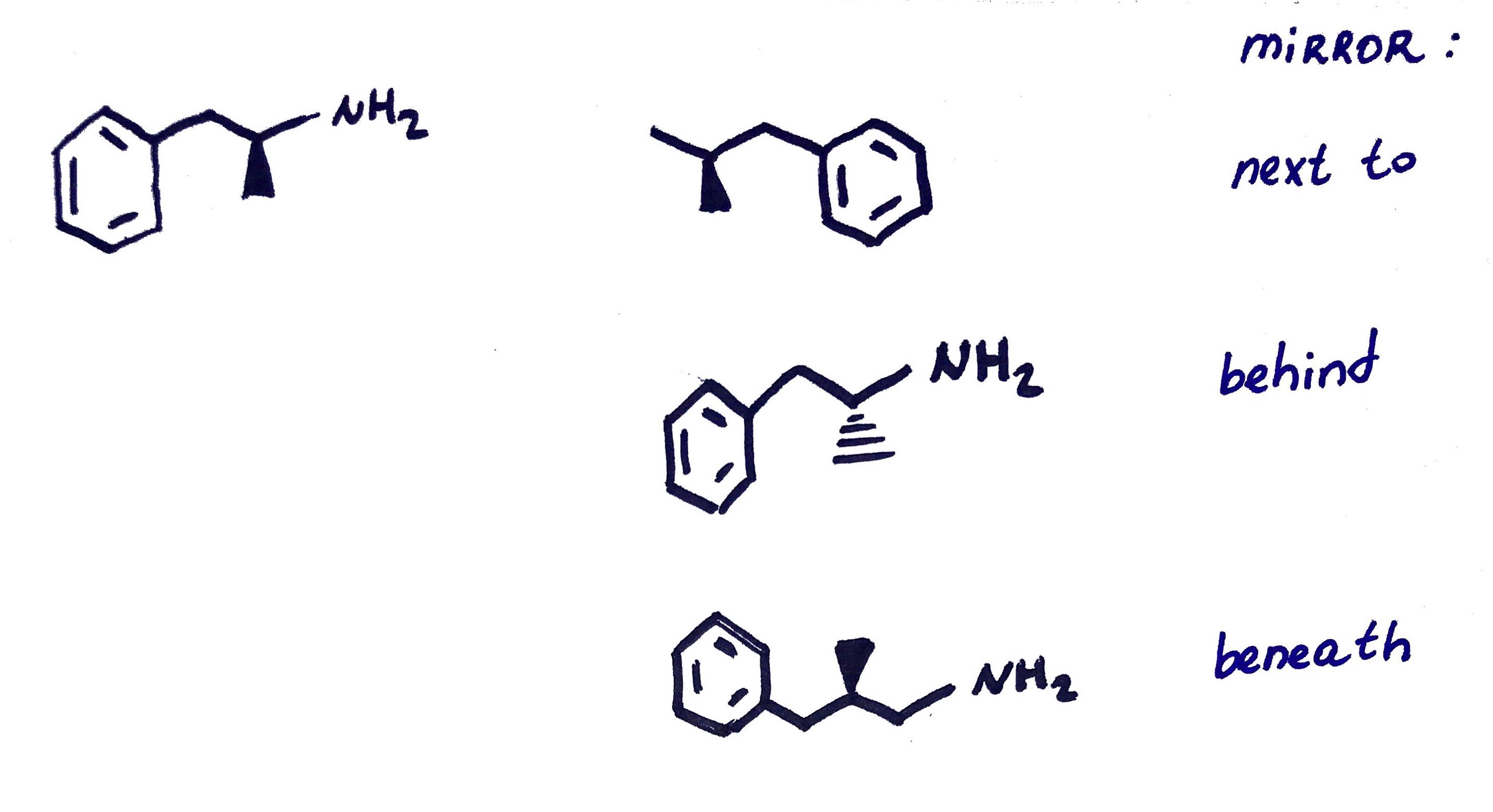
2. Chan-Ingold-Prelog
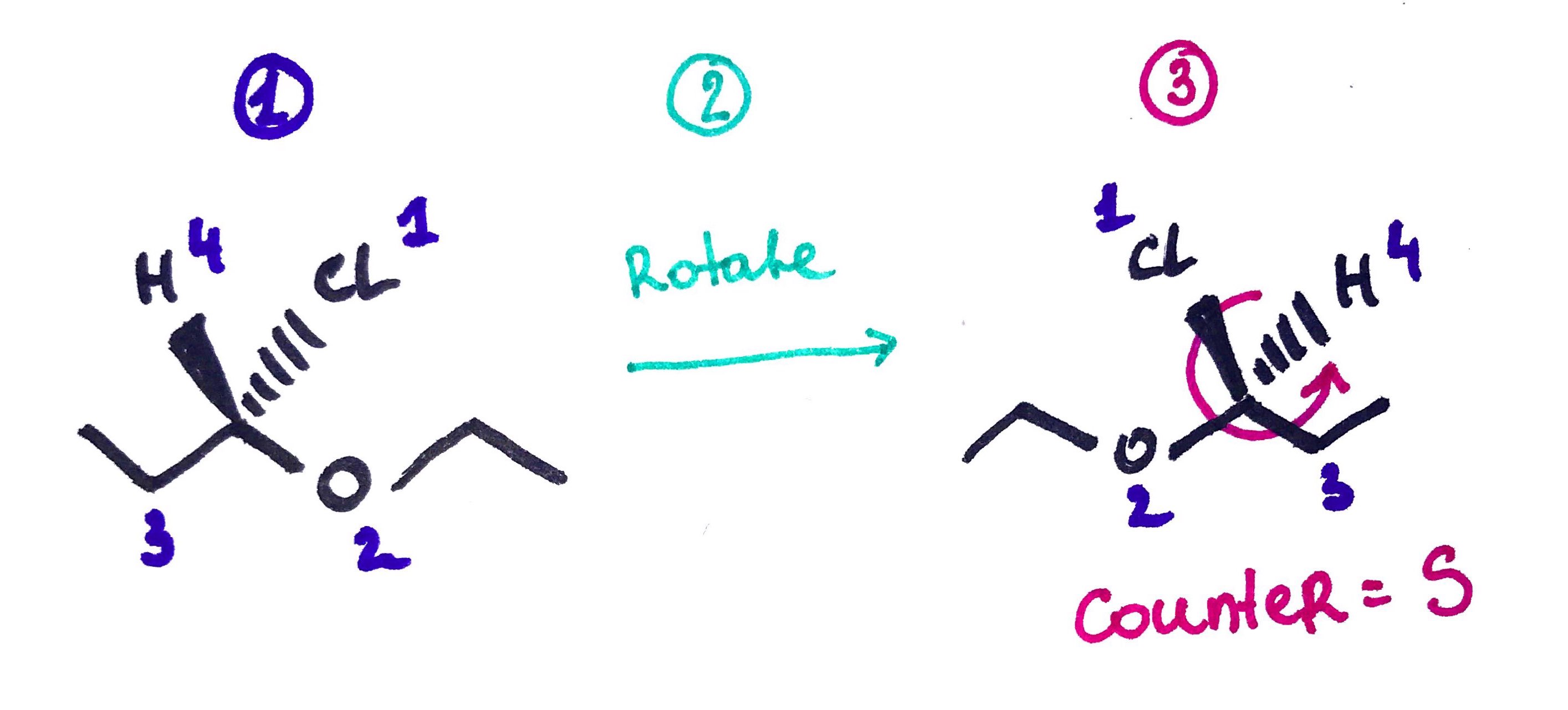
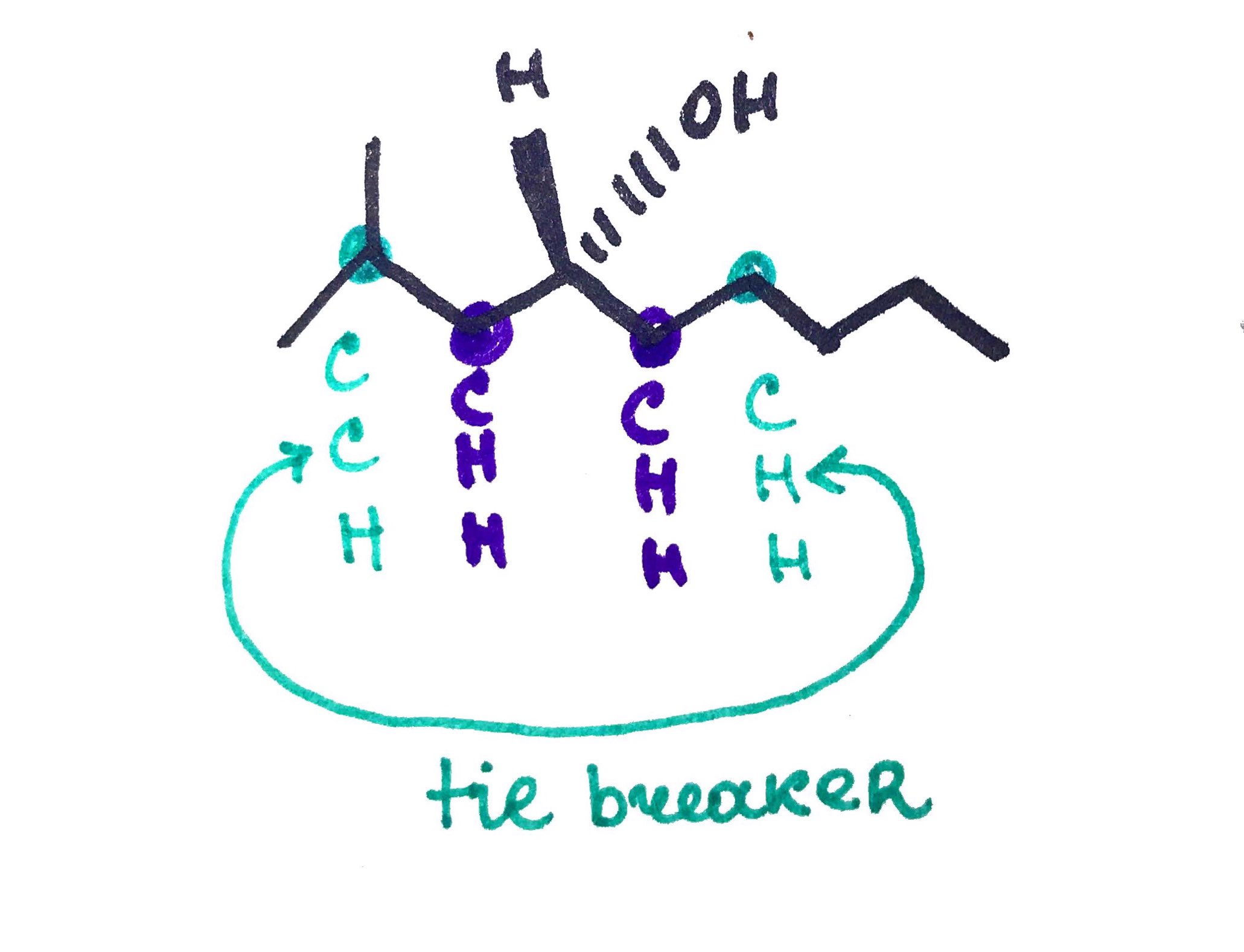
- Assign Priorities based on highest atomic number.
- Rotate the mocleule, so that 4th priority is on the dash(beghind the page).
- See if sequnce 1,2,3 is:
Clockwise = R
Counter Clockwise = S
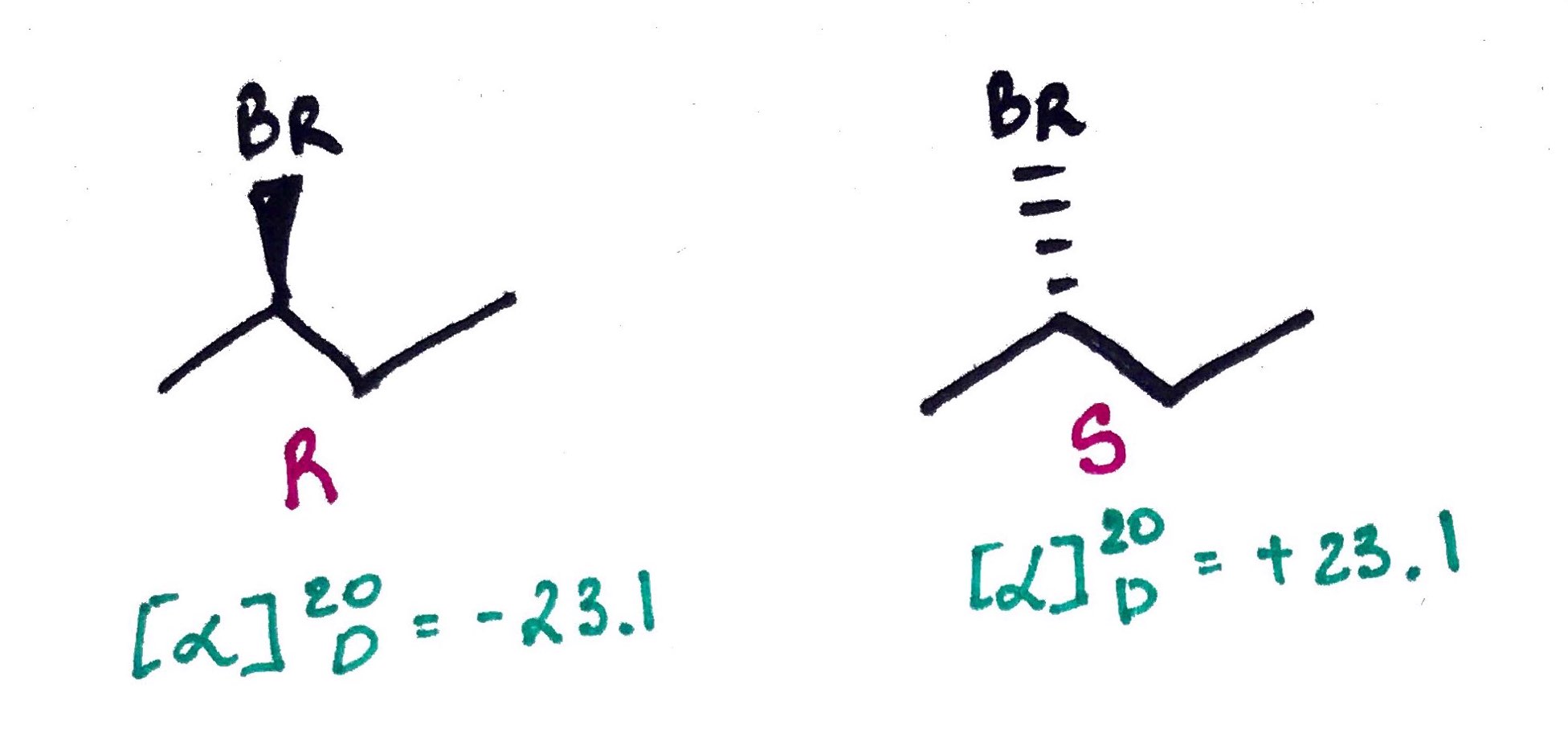
3. Optical Activity.
Enantiomers exhibit identical physical properties, however they rorate polorized light diferentley.
L = -
Specific Rotation [α] = α / c * L
α - observed rotation
c - concentration (g/ml)
L - pathlength
Beware:
Temperature and Wavelenght can affect [α], but they are not included in the formula, instead they are reported.
In the example below T = 20C and; D stands for D line of sodium (589nm)
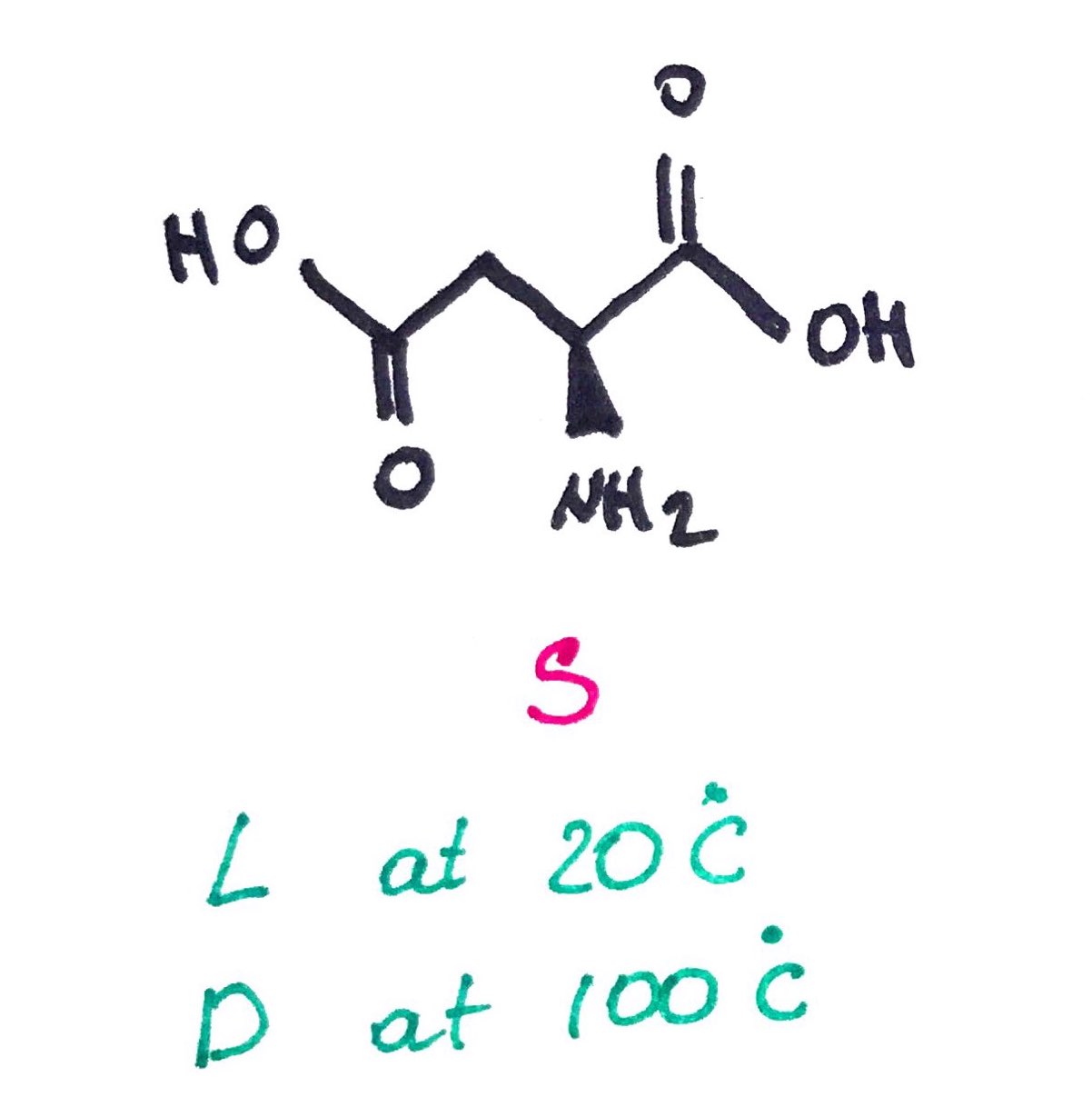
Beware:
L and D does NOT correlate with R and S. In the example below, the same compound changes light rotation depending on the T.
4. Enantiomeric Excess
EE - is a mesurment of the purity of the compound.
How to calculate it?
experimental/observed α = -53
standard/pure α = -45
1.
%ee = 45/53 * 100% = 85%
2.
85% - pure
15% - racemic mixture (7.5% of each D and L)
3.
85% + 7.5% = 92.5% of desired product.
7.5% of contaminant enantiomere.