Molecular Orbital Theory
In chemistry, Molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. Electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.
MO theory can more accurately explain the bonding in the structures with resonance. Such as N2+
1. Intro
Simple example below, shows MO for H2 molecule and why He2 cannot exist
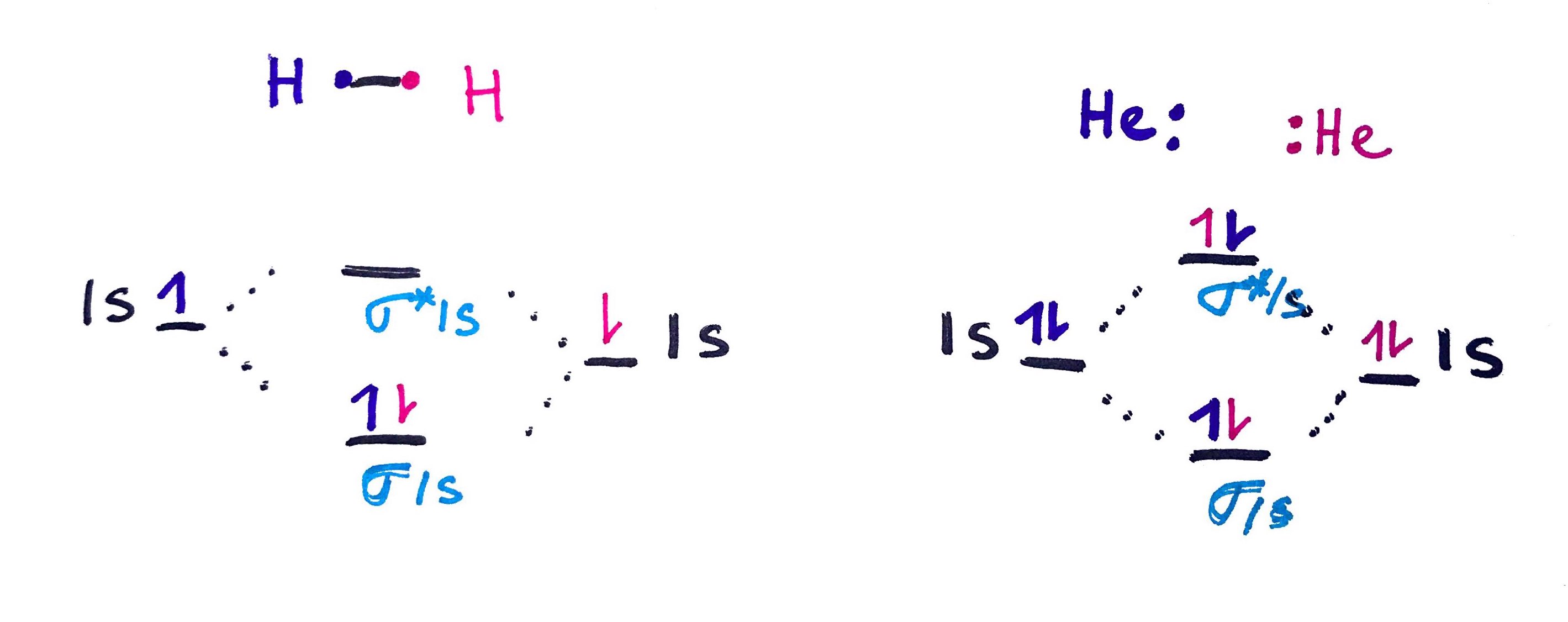
2. MO for diatomic moleculs
For 2π there are two diffrent MO diagrmas for (O2, F2) and (B2, C2, N2):
For O2 and F2:
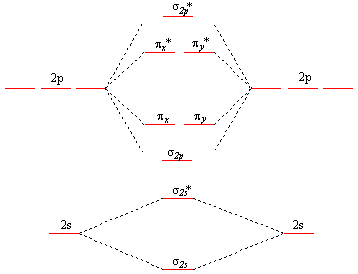
For B2, C2, N2:

Practice
Construct MO for N2 and N2+
N electron config = 1s2, 2s2, 2p3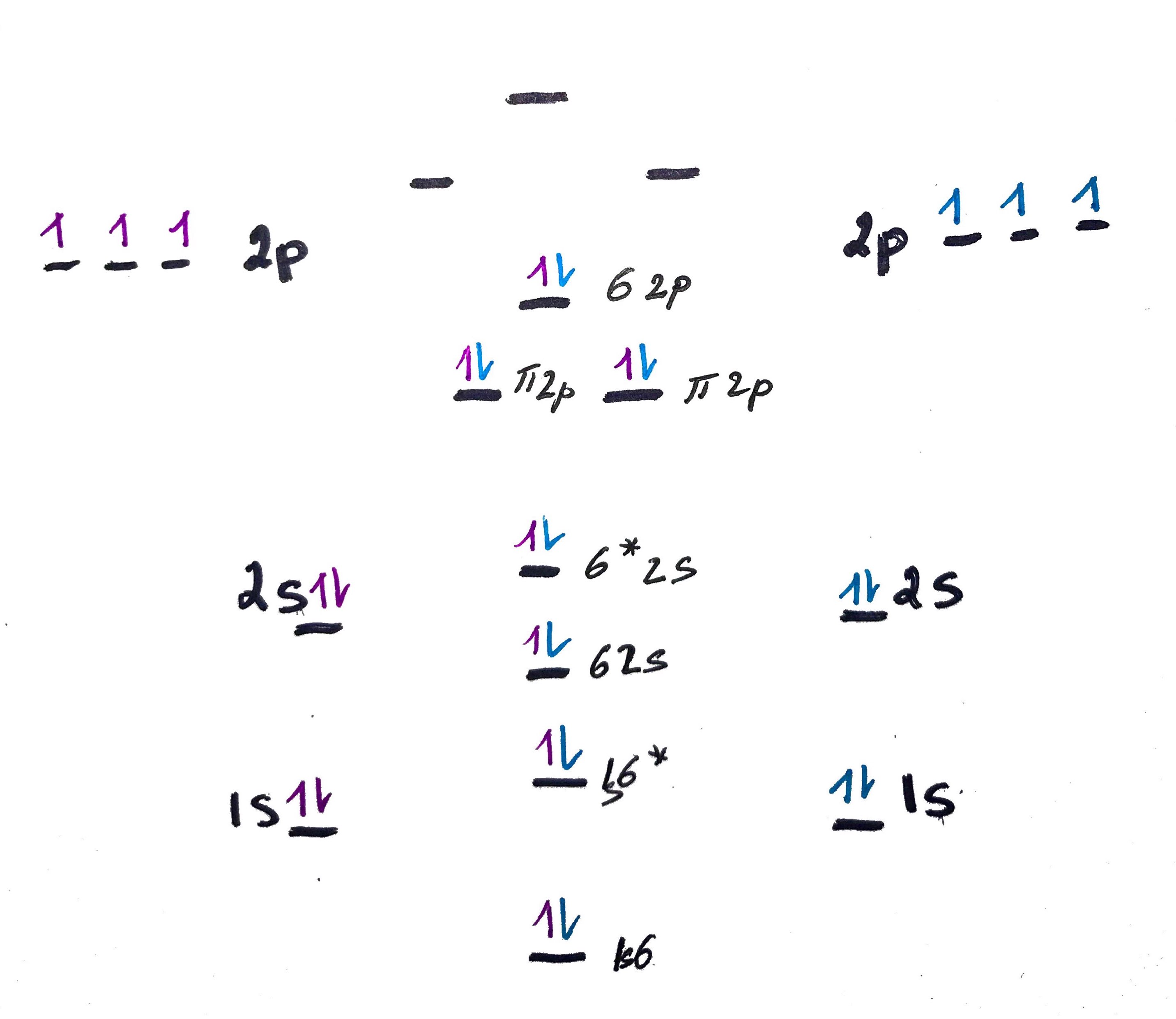
Note, for N2+ just remove 1e from the top σ2p. Thi explains why N2+ is in resonanse.
3. HOMO and LUMO
HOMO - highest occupied molecular orbitalLUMO - lowest unoccupied molecular orbital
